Respirators - Respirator Care
On this page
Why is it important to care for a respirator?
Back to topThe function of a respirator is to protect the wearer from respiratory hazards. Personal protective equipment is typically the last line of defence. Employers are required to provide workers with suitable personal protective equipment, while workers have the responsibility to care for those devices. Without proper care, the protective qualities of the respirator could be compromised, potentially causing the worker to be exposed to hazards that could impact their health and safety. A checklist can help a worker properly inspect and care for a respirator. As a minimum, follow the manufacturer's recommendations for care of the respirator.
What is an example of a checklist for caring for my respirator?
Back to topChecklist for care of respirators
- Inspect the respirator before and after each use and during cleaning.
- Inspect equipment designated for "emergency use" at least monthly, and before and after each use.
Replace all cracked, torn, broken, missing, or worn parts (or replace the respirator entirely if it cannot be repaired). Any respirator that needs repair should be identified as out of service (such as with a tag). - Follow the manufacturer's instructions and consult CSA Standard Z94.4-18 (R2023) Selection, Use and Care of Respirators for information on the care, maintenance, and storage of respirators.
Facepiece
- Ensure that no holes or tears are present.
- Inspect for cracked, scratched, or loose-fitting lenses and missing gaskets.
- Ensure that the metal nose clip forms easily over the bridge of the nose on disposable respirators.
- Make sure the facepiece edges are not rippled or distorted.
- For a full facepiece respirator, check for missing mounting clips.
Head strap/harness
- Check webbing for breaks.
- Look for deterioration of elasticity or fraying edges.
- Test excessively worn head harness.
Inhalation and exhalation valves
- Ensure the valve and valve seat are free of dust particles or dirt that may cause a poor seal or reduce efficiency.
- Replace any missing or defective valve covers.
Filter elements
- Ensure that the filter and mask are certified for use together.
- Check the filter to see that it is approved for the hazard.
- Inspect both the filter threads and facepiece threads for wear, make sure they are screwed together properly, and there is no cross-threading.
- Check the filter housing for cracks or dents.
- Check the end-of-service life indicator for gas masks. Check the expiration date. Some visibly soiled respirators (such as N95 masks) cannot be cleaned and should be replaced.
Air supply system
- Inspect the air-supply hose and end-fitting attachments for breaks, cracks, or kinks.
- Test the tightness of connections.
- Ensure the proper operation and condition of all regulators, valves, or other airflow device.
- For compressors, monitor the operation of air-purifying elements and carbon monoxide or high-temperature
alarms . - Check seams in a suit or blouse for rips and tears.
- Ensure that protective screens are intact and fit correctly over the facepiece (abrasive blasting hoods and blouses).
Respiratory battery pack
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions for charging and discharging.
- Use chargers designed for the battery type.
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions for charging and discharging.
- Ensure that the batteries are charged appropriately before using them.
Repair, cleaning, and storage
- Do not clean with solvents.
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions.
- Wash with a mild dish detergent or a combination of detergent and disinfectant. Use a brush and warm water (49-60ºC or 120-140ºF).
- Rinse with clean water, or rinse once with a disinfectant and once with clean water. The clean water rinse removes excess detergent or disinfectant that can cause skin irritation or dermatitis.
- Dry on a rack or clean surface. Position the respirator so that the facepiece rubber will not "set" crookedly as it dries.
- Store the respirator at the end of each shift to protect it from dust, sunlight, heat, extreme cold, excessive moisture, and chemicals.
- Clean and disinfect respirators after each use, where appropriate.
- Permit only trained and qualified personnel to repair respirators.
- Do not mix parts from different manufacturers.
- Record all repairs and inspections.
- Remove dirt.
Check for distortion caused by improper storage.
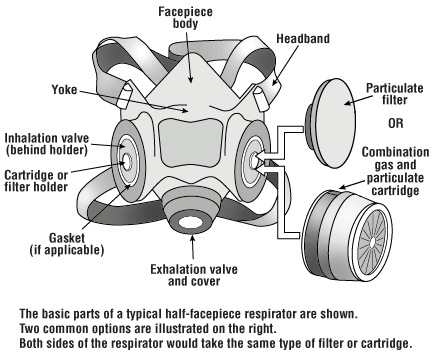
Figure 1 - Sample Half-face Respirator
What is an example of a checklist for caring for my self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA)?
Back to topChecklist for self-contained breathing apparatus (SCBA)
- Inspect the SCBA unit before each use. Test and clean after each use.
- Inspect the equipment designated for "emergency use" at least monthly and after each use.
- Follow the manufacturer's instructions and CSA Standard Z94.4-18 (R2023) for care and maintenance.
- Permit only trained, manufacturer-certified personnel to maintain SCBA.
- Do not mix parts from different manufacturers.
- Maintain a complete record for each SCBA facepiece and cylinder.
Facepiece
- Disconnect the facepiece from the breathing apparatus. Wash alone in warm (49-60 ºC or 120-140 ºF) soapy water using a mild dish detergent.
- Rinse the water through the facepiece by placing the palm of your hand over the breathing tube connector on the exhalation valve body.
- Remove excess water with a paper towel or lint-free cloth.
- Allow to air dry.
- Sanitize according to the manufacturer's instructions.
- Check for tears or cracks in the rubber.
- Check the head strap for deterioration.
- Examine lenses for cracks, excessive scratching, or other deformities.
- Check rings and clamps securing the lens for bends or bulges in the metal.
- Check the exhalation valve to ensure that it is properly located and that the valve cover is in place.
- Test the exhalation valve. Block the air intake opening and exhale gently. If the exhalation valve is not working properly, a heavy blow-by will be felt at the temples. Inhale and a partial vacuum will be formed.
- Do not mix demand and pressure-demand facepieces and regulators.
Regulator
- Check the regulator, breathing-tube threads, pressure gauge, and bypass and mainline valves for impact damage.
- Store with the cylinder valve completely closed.
- Bleed off air remaining in the regulator after each use, following manufacturer's instructions.
Breathing tube
- Stretch the breathing tube and check for cracks, tears, and punctures.
- Check gaskets.
- Check clamps and rings to ensure that they are tight, properly located, not dented, and not excessively corroded.
- Wash the breathing tube separately and allow to air dry. If it is permanently attached to the facepiece, allow the breathing tube to dry for several days before
use .
High-pressure hose
- Check the hose for cuts, bubbles, and abrasions.
- Check the fitting between the high-pressure hose and the regulator for damage.
Audible alarm
- Check the audible alarm for damage.
- Clean bells or whistles.
- Ensure that the alarm is working. If it does not go off when the pressure reaches 20-25% of service time, the unit is defective. Remove it from service.
Backpack
- Inspect the straps of the backpack for excessive wear, broken stitching, and damaged or missing hardware.
Cylinder
- Ensure cylinders are hydrostatically tested as set out in CSA Standard Z94.4-18 (R2023), Selection, Use and Care of Respirators.
- Inspect for cuts or gouges that can cause the unravelling of the composite fibres of the cylinder overwrap.
- Check unwrapped cylinders for impact damage.
- Check for evidence of exposure to heat. Look for discoloured paint or melted gauge lenses.
- Ensure the air meets the quality standards set out in CSA Standard Z180.1-13 (R2018), Compressed Breathing Air and Systems.
Cleaning the rest of the unit
- Remove backpack, cylinder, and regulator assembly.
- Clean with water or soapy water.
- Wipe the regulator, high-pressure hose, audible alarm, air cylinder, backpack, and harness with a damp cloth.
- Dry with a cloth.
Contact the government department responsible for health and safety in your jurisdiction for additional information on regulatory requirements for respiratory protection.
- Fact sheet last revised: 2024-09-25
