Working in a Standing Position - Working in Standing/Sitting Positions
On this page
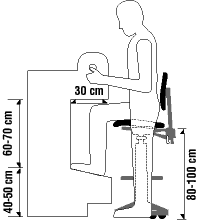
What is an example of a workstation for sitting/standing?
Back to topContinuous standing or sitting while working is a common source of discomfort and fatigue. Frequent changes of body positions, including alternating between sitting and standing, helps to avoid fatigue.
- Adjust the workstation to the proper height for the user. Refer to the document Working in a Standing Position for more information.
- Use an ergonomic chair or alternative chair with an adjustable seat height.
- Adjust the chair seat height to suit the user.
- Use a footrest which helps the worker bend the knees at a 90° angle (or slightly higher) while sitting on the chair.
Back to top
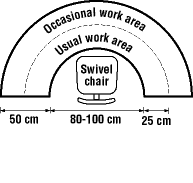
What are examples of a chair for sitting/standing workstations?
Back to topWhenever possible, a worker should be able to work sitting or standing at will.
- Ensure that the seat has a minimum width of 45 cm (about 18 in.).
- Choose back rests that are contoured vertically and horizontally.
- Use a seat covering of non-slip, breathable fabric.
- Select seat padding that is about 2-3 cm (1 in.) thick.
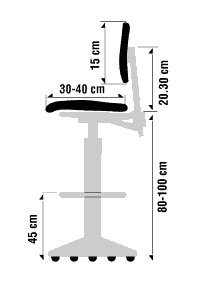
- Ensure that chairs have a back support.
- Use arm rest if appropriate. Some individuals do not use an arm rest because leaning on the arm rest can put pressure on the underside of the arm. In other situations, the armrests may not allow the chair to be close enough to the work surface, which may result in overreaching.
- Provide a chair for resting purposes even when work can only be done standing.
- Provide a chair that can fold up and be stored out of the way where space is limited.
- Fact sheet last revised: 2022-11-30

